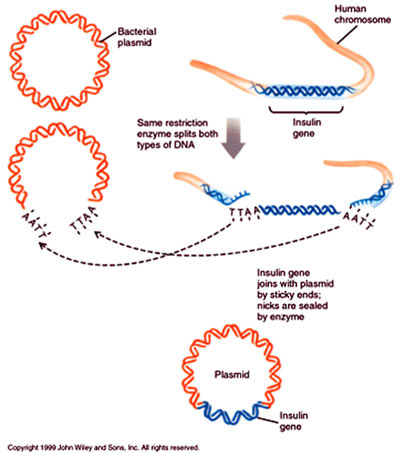
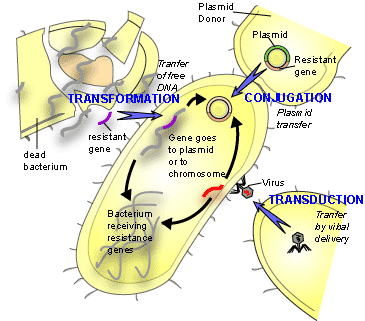
Background: Genetically modified organisms began with the discovery of DNA in 1953. Bacteria - the first organisms to be genetically engineered - are used for replicating and altering genes that are then introduced into plants or animals. The genetically engineered bacteria have found applications in various areas:
|
Regulation and Policies: USDA’s Jurisdiction Over GMOsGenetically modified products that would be subject to the PPA (Plant Protection Act) regulations would be those that had been “altered or produced through genetic engineering, if the donor organism, recipient organisms, or vector agent belongs to any genera or tax designated in 340.2 and meets the definition of plant pest (bacteria and fungi).” In other words, in order to trigger USDA oversight, genetic engineering must be involved and the donor, recipient or vector must be a plant pest. Innovators: Genentech is considered the founder of biotechnology medicine. They are using human genetic information to make medicine for patients with life-threatening diseases or conditions. They make high-quality medicine in a responsible and ethical manner. Genencor is one of the largest developers of enzymes in the world and is located in more than 40 countries. They also reduce environmental impact through all their industries like food, transportation fuels, and laundry detergent. Amgen has been a leader in biotechnology since1980. They produce safe medicine for plants and patients. They help millions of patients around the world with the advances in recombinant DNA and molecular biology. |
Issues: Pros:
 |
||