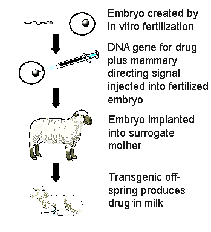
Background: Genetically engineered animals were first developed in the 1980s. Genetically engineered animals or 'transgenic" animals are designed to help researchers diagnose and treat human diseases. The first transgenic animals were produced by injecting DNA into eggs. Then, implanting the eggs in animals and then waiting weeks or months to see if any offspring had incorporated the extra DNA. A genetically engineered animal is an animal that carries a known sequence of recombinant DNA in its cells, and which passes that DNA onto its offspring. The purpose of genetically engineered animals is to create animals with special characteristics. Animals Citation 1, 6, 8, 13 Innovators: BayBio has an Agricultural Biotech Sector that uses plants and animals for genetic traits. They are also used for human therapeutics. (Animals 12) Scientists at Nexia Biotechnologies, a company based in Montreal, isolated the gene for silk protein from a spider capable of spinning silk fibers which is one of the strongest yet most resilient substances known. They then inserted it in the genome of a goat’s egg prior to fertilization. Animals Citation 13 Recombinant bovine growth hormone (also known as rBGH or rBST is a genetically engineered drug produced by the Monsanto Corporation. It is injected into dairy cows to induce them to increase milk production, typically by 5-15%. It's estimated that 15-20% of the cows in the United States are injected with this hormone. It was approved by the FDA in 1993. The concern is that there is an increased cancer risk and can give cows a painful udder infection. |
Regulation and Policies: The FDA states, "The FFDCA defines "articles (other than food) intended to affect the structure or any function of the body of man or other animals" as drugs. An rDNA construct that is in a GE animal and is intended to affect the animal's structure or function meets the definition of an animal drug, whether the animal is intended for food, or used to produce another substance. Developers of these animals must demonstrate that the construct and any new products expressed from the inserted construct are safe for the health of the GE animal and, if they are food animals, for food consumption." "The FDA has adopted new rules that allow companies to sell genetically modified animals and their products on the market, and stating that the DNA of such animals is private property that can be held under patent. To be approved, any genetically modified animal product must be proven to the FDA's satisfaction to be safe for human use in a process similar to that undergone by new drugs." "Clinical trials like those needed for drugs will not be required, however. The FDA must also show that any genetically modified animal is healthy. No FDA approval will be required for cloned animals or those intended only for research or as pets." Animals Citation 4 |
Issues: Pros:
Cons:
(Animals 5)
|
||